Basic Human anatomy & physiology
basic human anatomy and physiology?
Anatomy is the study of the structure and relationship between body parts. Physiology is the study of the function of body parts and the body as a whole. ... Gross (macroscopic) anatomy is the study of body parts visible to the naked eye, such as the heart or bones.
basic human anatomy?
Basic anatomy is one of the three major subdivisions of human anatomy (with Gross Anatomy and Histology). It is actually a code to understand the terminology and concepts of anatomy. Basic anatomy introduces the students to the definitions, terminology and basic theme of anatomy.
Andreas Vesalius
The Fabrica of Andreas Vesalius: The Father of Modern Anatomy and His Most Famous Work. Andreas Vesalius was a Belgian born anatomist and physician, born in 1514 into a family of physicians. He is considered the father of modern anatomy and his work the beginning of modern medicine.
Cells of the Body
Cells are the basic building blocks of the human body and the bodies of all other living species, including other mammals and plant life. Some living organisms like the amoeba and the paramecium are one celled, or unicellular, living bodies, but, for the most part, living organisms are made up of trillions and trillions of cells.
There are two different types of cells. These are prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes are cells that don't have organelles or a nucleus. Bacteria are an example of a prokaryote cell. Eukaryotes are cells that have a nucleus containing genetic material and organelles, as described below. The cells of the human, animals and plants are examples of eukaryote cells.
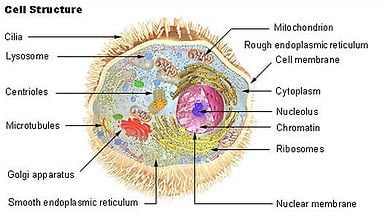
The generalized structure and molecular components of a cell
As shown in the picture above, cells consist of a:
- Cell wall
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Cytoskeleton
- Organelles
The cell's cell wall protects the cell membrane and the cell from threats in its external environment; the external environment of the cell is referred to as extracellular. In contrast, the intracellular environment is the internal environment of the cell.
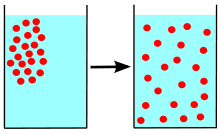
Ions are electrically charged molecules such as electrolytes, in the human body. Electrolytes that have a negative electrical charge are called anions and electrolytes that have positive electrical charge are called cations. Electrolytes and the levels of electrolytes play roles that are essential to life. For example, these electrically charged ions are necessary to contract muscles, to move fluids within the body, they produce energy and they perform many other roles in the body and its physiology.
Electrolytes, similar to endocrine hormones, are produced and controlled with feedback mechanisms that control low and high levels of electrolytes.
The body's cations, or positively charged electrolytes, that move in and out of cells with diffusion, are listed below:
- Sodium which is abbreviated as Na+
- Potassium which is abbreviated as K+
- Calcium which is abbreviated as Ca+
- Magnesium which is abbreviated as Mg+
The body's anions, or negatively charged electrolytes, that move in and out of cells with diffusion, are listed below:
- Chloride which is abbreviated as Cl -
- Hydrogen phosphate which is abbreviated as HPO4-
- Bicarbonate which is abbreviated as HCO3-
- Sulfate which is abbreviated as SO4-
Contact us ;-D/354 Vibhuti Khand Gomti Nagar,Lucknow 226040
Visit us ;-www.rhec.in
Phone No :-7355268808,9415787135,6388843372
Comments
Post a Comment